Estimating Duties and VAT for EU Imports

You do not want surprises when you shop from other countries. Estimating duties and VAT estimation for EU imports helps you plan your costs. It also stops hidden fees from showing up. Many shoppers get customs charges they did not expect. 58% pay extra costs, and 75% think before buying again. To estimate duties and VAT the right way, follow these steps:
Step | Description |
|---|---|
HS Codes | Make sure you classify your goods right. |
Customs Value | Add the invoice price, shipping, and insurance together. |
Tariff Rate | Look at the EU schedule for your product. |
Value Added Tax (VAT) | Find the correct rate for your country. |
Compliance and Documentation | Get invoices and declarations ready. |
Knowing these steps keeps you safe if you import to the EU or the UK.
Key Takeaways
Figure out duties and VAT before you buy things from other countries. This helps you avoid surprise costs and waiting longer for your items.
Use the right HS code to sort your goods. This helps you find the correct duty rate and makes sure you follow the rules.
Add up the invoice price, shipping, and insurance to get the customs value. This total is important for working out the right duty and VAT.
Look up the newest duty rates in the EU Tariffs Database. This makes sure you use the latest info for your imports.
Keep all invoices and customs papers in order. This helps you follow the rules and can help you get back import VAT if you run a business.
Duties and VAT Estimation Basics
What Are Import Duties?
Import duties are taxes you pay when you bring goods into the EU from countries outside the EU or UK. These taxes help protect local businesses and make sure everyone follows the same rules. Customs authorities across the EU use the Common Customs Tariff to decide how much you owe. This tariff sets the same rates for all member states, so you will pay the same import duties whether your package arrives in Spain, Germany, or France. The amount depends on what you buy and where it comes from. The rules of origin also play a role, as they help customs decide if your goods qualify for special duty rates.
Import duties apply to goods from non-EU countries.
The Common Customs Tariff sets the rates for all EU countries.
Customs authorities work together to make sure the rules are fair.
What Is Import VAT?
Import VAT is another tax you pay when goods enter the EU or UK. You pay this tax at the same rate as if you bought the item in your own country. For example, the standard rate in the UK is usually 20%. Customs collect import VAT before they release your goods. This tax makes sure imported products do not have an unfair price advantage over local items. Import VAT is a big part of your total import costs, so you need to include it in your duties and vat estimation.
Why Estimation Matters for EU Imports
You need to estimate duties and VAT before you shop from outside the EU or UK. If you skip this step, you might face extra charges or delays. Many online shoppers do not pay VAT or import duties, which leads to lost public income and unfair competition. In fact, more than 60% of items sent by post do not have these taxes paid. Private carriers have much higher compliance rates. Accurate duties and vat estimation helps you avoid surprises and supports fair trade. The EU has made new rules to make VAT collection easier for online shopping. Platforms like Fishgoo help you follow these rules, so you can shop with confidence and stay in compliance. When you understand import vat vs import duty, you can plan your budget and enjoy a smooth shopping experience.
Types of Import Duties in the EU

When you bring goods into the EU or UK, you may pay different import duties. Each type changes your total cost in its own way. If you know about these types, you can plan better and avoid extra charges.
Ad Valorem Duties
Ad valorem duties are the most common kind. Customs set these as a percent of your goods’ customs value. This value is the price, insurance, and shipping added together. For example, if you buy a jacket for $100 and the duty rate is 12%, you pay $12 in duties. Most goods imported to the EU use this rule. This way, the duty matches what your item is really worth.
Specific Duties
Specific duties are not based on value. Customs charge a set fee for each unit, like per kilogram or per liter. You see this with things like grains or alcohol. Sometimes, there are special rules. Goods for trade fairs or music shows can enter for a short time without paying duties. Some items, like aircraft parts or oil platforms, get lower or no duties if used for certain jobs.
Duty Type | Description | Common Cases |
|---|---|---|
Temporary Admission | Goods can enter for up to 24 months with duty relief. | Trade fairs, music shows |
End-use | Goods released at reduced or zero duty for special uses. | Shipbuilding, civil aviation, oil/gas platforms |
Compound Duties
Compound duties use both ad valorem and specific duties. You pay a set fee for each unit and a percent of the value. For example, shoes might have a $5 fee per pair plus 10% of their value. The EU uses compound duties a lot for farm products. This helps local farmers and keeps prices steady.
Compound duties = set fee per unit + percent of value
Example: $5 per pair of shoes + 10% of value
Used often for farm imports
When Each Duty Type Applies
The duty you pay depends on what you import and where it comes from. Here is a quick guide:
Description | |
|---|---|
Standard import duty | Percent of value, used if there is no special rule. |
Preferential origin | Lower or no duties because of trade deals. |
Anti-dumping duty | Stops very cheap imports from hurting local sellers. |
Countervailing duty | Fights unfair help from the other country’s government. |
Safeguarding duties | Protects local businesses from too many imports at once. |
Quotas | Limits how much can come in at lower rates. |
Excise duty | Extra tax on things like alcohol or tobacco. |
Agricultural duty (EU only) | Flat fee per tonne for things like grains. |
If you know which duties you might pay, you can guess your total costs before you buy. This helps you shop from other countries with more confidence.
Calculate Import Duties
When you buy things from other countries, it is good to know how to calculate import duties. This helps you not get surprised by extra costs at the border. You can use a simple process to guess your total costs before your package gets to the EU or UK. Platforms like Fishgoo make this easier. They give you product links and clear order details. Here is how you can figure out duties and VAT step by step.
Find the HS Code
First, you need to find the right HS code for your product. The HS code is a special number that customs uses to sort goods. This number tells you the duty rate and if there are any special rules for your item.
If you do not know the code, you can ask customs for help.
The Customs tariff database lets you search for HS codes and commodity codes.
If you want an official answer, you can ask for Binding Tariff Information (BTI) from customs.
The General Rules of Interpretation (GRI) help you pick the best HS code for your product.
Tip: If you use Fishgoo, you can paste your product link into the platform. The system will help you find the right group, so it is easier to get the HS code.
Determine Customs Value
Next, you need to know the customs value of your goods. Customs value is the amount customs uses to figure out import duties. This value usually has the price you paid, shipping, and insurance up to the EU or UK border.
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Customs uses the real price you paid for the goods. This is the main way. | |
Transaction Value of Identical/Similar Goods | Customs checks the value of similar items brought in recently. |
Deductive Value Method | Customs uses the EU or UK selling price, minus duties, transport, and markups. |
Computed Value Method | Customs adds up production costs, labor, materials, and a fair profit. |
Fallback Method | Customs uses this only if other ways do not work, following WTO rules. |
Most people use the transaction value method. You add the invoice price, shipping, and insurance together. This total is your customs value.
Duty Rate Lookup
After you know your HS code and customs value, you need to find the right duty rate. The EU uses the TARIC database to show duty rates. This database has all the rules and tariffs for goods coming into the EU. You can search by HS code to see the rate for your product.
Note: Duty rates can change depending on where the product comes from. Trade deals may lower or remove duties for some countries. Always check the newest rates before you buy.
Duty Calculation Formula
Now you can figure out import duties with a simple formula. Start with your customs value. Multiply this by the duty rate you found in the TARIC database. If your product uses a specific duty, like per kilogram, use the set fee instead.
Formula:
Import Duties = Customs Value × Duty Rate
If your product has both ad valorem and specific duties, add both numbers together. Some products, like shoes or farm goods, use this mixed way.
Example: Duties on a Fishgoo Order
Let’s look at a real example with a Fishgoo order. Imagine you want to buy sneakers from China and send them to the UK.
Find the HS Code:
You paste the product link into Fishgoo. The platform helps you find the sneakers’ HS code, like 6403.99.Determine Customs Value:
The sneakers cost $80. Shipping and insurance add $20. Your customs value is $100.Duty Rate Lookup:
You check the TARIC database. The duty rate for sneakers is 16%.Duty Calculation Formula:
Import Duties = $100 × 16% = $16Check for Additional Duties:
No extra duties are needed here.Prepare Your Customs Declaration:
You include the invoice, shipping details, and HS code in your customs declaration. This helps your package move through the border easily.
Summary:
You pay $16 in import duties for your sneakers. You also need to figure out VAT, which is the next step. By following these steps, you can guess your total costs and not get surprised when shopping with Fishgoo.
This process helps you figure out import duties for any product coming into the EU or UK. You can use these steps for electronics, clothes, or anything else. Good duties and VAT estimation makes shopping easy and worry-free.
Import VAT Calculation
VAT Rate in the EU
You need to know the correct rate before you calculate import vat in the eu. Each country sets its own rate for value added tax. Most countries use a standard rate, but some offer reduced or super reduced rates for certain products. You must check the rate for your destination to stay in compliance.
Here is a table showing the standard, reduced, and special rates for import vat in the eu:
Country | Standard Rate | Reduced Rate | Super Reduced Rate | Parking Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Austria | 20% | 10% / 13% | - | 13% |
Belgium | 21% | 6% / 12% | - | 12% |
Bulgaria | 20% | 9% | - | - |
Cyprus | 19% | 5% / 9% | - | - |
Czechia | 21% | 12% / 0% | - | - |
Germany | 19% | 7% | - | - |
Denmark | 25% | 0% | - | - |
Estonia | 24% | 9% | - | - |
Greece | 24% | 6% / 13% | - | - |
Spain | 21% | 10% | - | - |
Finland | 25.5% | 10% / 14% | - | - |
France | 20% | 5.5% / 10% | 2.1% | - |
Croatia | 25% | 5% / 13% | - | - |
Hungary | 27% | 5% / 18% | - | - |
Ireland | 23% | 9% / 13.5% | 4.8% | - |
Italy | 22% | 5% / 10% | 4% | - |
Lithuania | 21% | 5% / 9% | - | - |
Luxembourg | 17% | 8% | 3% | 14% |
Latvia | 21% | 5% / 12% | - | - |
Malta | 18% | 5% / 7% | - | - |
Netherlands | 21% | 9% | - | - |
Poland | 23% | 5% / 8% | - | - |
Portugal | 23% | 6% / 13% | - | 13% |
Romania | 21% | 11% | - | - |
Sweden | 25% | 6% / 12% | - | - |
Slovenia | 22% | 5% / 9.5% | - | - |
Slovakia | 23% | 19% | 5% | - |
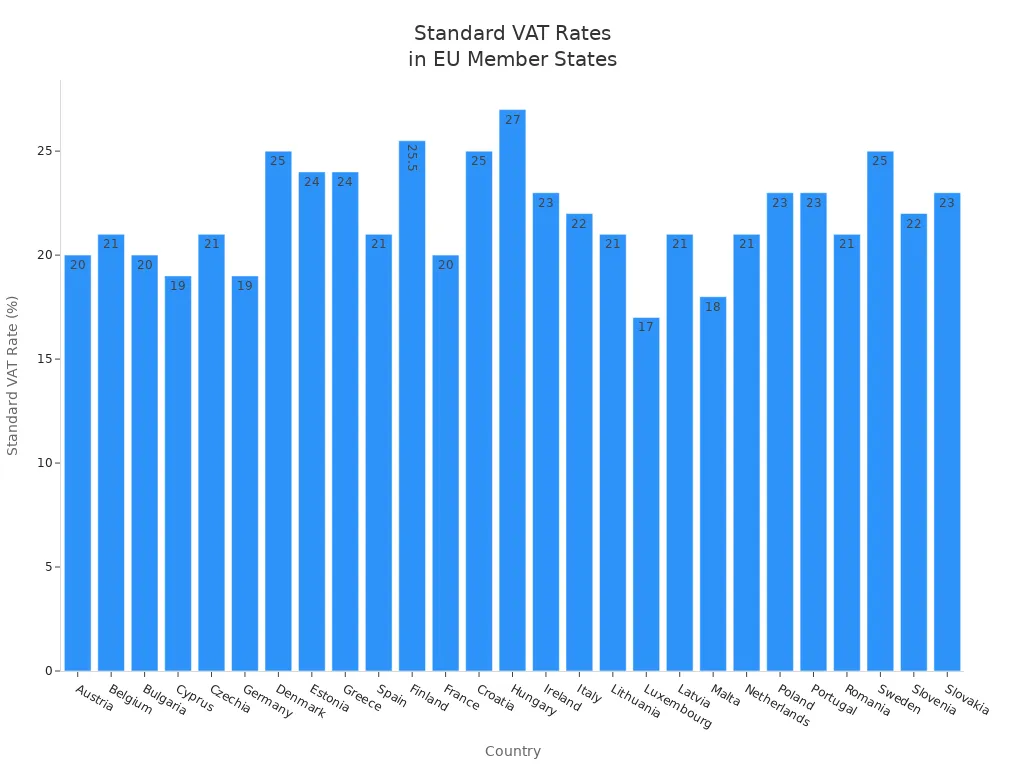
You see that countries like Hungary and Denmark have higher rates, while Luxembourg has the lowest standard rate. You must use the correct rate for your country to ensure vat compliance. If you use the import one-stop shop, you can simplify reporting and payment for cross-border sales.
VAT Calculation Formula
You must know how import vat is calculated to get your full landed costs. Customs authorities use a clear formula. You add the value of the goods, any duties, and then multiply by the correct vat rate. This gives you the total import vat you must pay.
Here is a simple table showing the formula:
Component | Description |
|---|---|
Value of the Goods | The price of the goods you import |
Duty | Any import duties you must pay |
VAT Rate | The rate for your country and product |
Import VAT | (Value of the Goods + Duty) × VAT Rate |
Tip: You must include shipping and insurance in the value of the goods. This helps you get the full landed costs and stay in compliance.
If you import to the uk, you use the same formula. You must check the current rate for import vat in the uk. The standard rate is usually 20%. You can use postponed vat accounting to delay payment until your next vat return. This helps with cash flow and keeps you in vat compliance.
Example: Import VAT on a Fishgoo Shipment
Let’s walk through a real example so you see how import vat in the eu works for a Fishgoo order. You want to buy a smartwatch from China and ship it to Germany.
You check the total value of your shipment. The watch costs $120. Shipping and insurance add $30. Your total is $150.
You look up the customs duty. For smartwatches, the duty rate is 3%. You pay $4.50 in duty.
You add the duty to your shipment value. $150 + $4.50 = $154.50.
You check the vat rate for Germany. The standard rate is 19%.
You calculate import vat. $154.50 × 19% = $29.36.
You must pay $29.36 in import vat before customs releases your package. This amount is part of your full landed costs. You must keep all invoices and customs documents for compliance.
If you import to the uk, you follow the same steps. You use the standard rate for import vat in the uk. You can use postponed vat accounting to report and pay later. This keeps your business in vat compliance and helps you manage costs.
You must remember that import vat is not the same as duties. You pay both to get your goods released. You must use the import one-stop shop if you sell to multiple eu countries. This makes vat compliance easier and helps you avoid mistakes.
Note: You must check if your goods qualify for reduced rates. Some products, like books or medicines, use lower rates. You must always check the latest rules for duties and vat estimation.
You see that knowing how import vat is calculated helps you plan your budget. You avoid surprises and keep your business in compliance. You must include import vat in your landed costs every time you shop with Fishgoo or any other platform.
Reclaim Import VAT
Who Can Reclaim VAT?
You may wonder if you can reclaim import vat after bringing goods into the EU. If you run a business, you have a chance to get this money back. You must meet certain conditions to qualify. Here are some main points:
Your company is established in the Netherlands or another EU country.
You regularly import goods from countries outside the EU.
You keep clear records that show how much import vat you paid.
You also need to follow some rules. The country where you import goods may have its own laws about refunds. Your company must keep accurate documents and follow all compliance steps. The Incoterm you use for shipping can also affect if you can reclaim import vat. If you want to manage import vat effectively, always check the rules before you import.
If you import goods for business and keep good records, you can often reclaim import vat. This helps lower your total costs.
Steps to Reclaim Import VAT
You need to follow a few steps to reclaim import vat in the EU. Each country may have its own process, but the main steps are similar. Here is what you should do:
Identify which expenses had import vat. Check the rules in the country where you paid the tax.
Prepare all needed documents. You must have invoices, proof of payment, and your business registration papers. Make sure these meet the country’s standards.
Submit your refund application. Use the correct online portal for the country. Pay attention to language needs and deadlines.
If you import goods into the UK, you follow a similar process. Always keep your paperwork safe. If you know who pays import vat and follow these steps, you can reclaim import vat and save money for your business.
Glossary of Key Terms
When you bring goods into the EU, you will see many new words. Knowing these terms helps you not make mistakes. It also makes shopping easier for you. Here is a glossary that explains the most important words you will see when estimating duties and VAT.
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Direct Representation | A customs agent works for you, but uses your name. You are still responsible for all customs rules and payments. |
Indirect Representation | A customs agent works for you and uses their own name. Both you and the agent must follow customs rules together. |
A licensed expert who helps you with customs rules. They prepare documents, pay duties, and talk to customs officials for you. | |
Customs Declaration | A formal statement you give to customs. It lists details about your goods, like value, origin, and classification. |
Import Duty | A tax you pay when you bring goods into the EU. The amount depends on the value, type, and where your goods come from. |
A tax added to goods and services at each step of making or selling. You pay VAT on most imports into the EU. | |
Customs Valuation | The way customs figures out how much your goods are worth. Customs use this value to set duties and taxes. |
Single Administrative Document (SAD) | A standard form you use for customs declarations in the EU. It covers import, export, and moving goods through the EU. |
Importer of Record (IOR) | The person or company who makes sure imported goods follow all laws. They pay duties and taxes and file the right paperwork. |
Binding Tariff Information (BTI) | An official answer from EU customs that gives you a fixed tariff code for your goods. This helps you know the exact duty rate. |
Customs Clearance | The process of finishing all customs steps. You submit documents, pay duties, and follow rules so your goods can enter the country. |
Tip: If you use a platform like Fishgoo, you will see these words during your order and shipping. Knowing what they mean helps you track your package and understand your costs.
You can look at this glossary whenever you need to check a word or process. This knowledge helps you shop with confidence and avoid surprises when importing goods.
Tools and Resources for Duties and VAT Estimation
You can use special tools to estimate duties and VAT for your imports. These tools help you plan your money before your package comes. They also help you avoid surprise costs. Customs value is very important in these calculations. Customs officials decide this value when your goods first enter the EU. They use set rules to make sure the value is fair and matches what your goods are really worth.
Here are some steps you can follow to get the right duty rates:
Type in your product’s classification code, like HS, CN, or TARIC.
Look at the results to see the duty rate for your item.
You should remember that imports of goods must pay VAT. You pay this tax when your goods go through customs. The customs value is needed to figure out both import duties and VAT.
Many online calculators can help you guess these costs. You put in your product details, and the calculator gives you an answer. These tools work well for most items. But they do have some limits. The calculators need the right product details and HS codes. If you use the wrong code, your guess might be wrong. Some calculators do not work with special duties or rule changes. For example, VAT calculations need the correct customs duty rate, which can be hard to find. New laws can also change your final cost.
Tip: Always check your product’s HS code and customs value before using any calculator. Official databases give you the best and most correct information.
Here is a table of helpful resources for estimating duties and VAT:
Resource | Purpose | Website |
|---|---|---|
EU Tariffs Database | Find duty rates and rules | https://ec.europa.eu/taxation_customs/dds2/taric/taric_consultation.jsp?Lang=en |
UK Trade Tariff | Check duty rates for imports to the UK | |
Online Duty Calculators | Estimate duties and VAT | Various (search online) |
You can use these tools to make shopping easier. When you shop with platforms like Fishgoo, you get extra help with product links and order details. This makes it simple to find the right codes and rates.
You can figure out duties and VAT for imports by using simple steps. First, sort your goods into the right group. Next, check the customs value for your items. Then, use the newest rates to get your numbers right. Platforms like Fishgoo help you not make mistakes. They give expert help and real-time updates to make things easier.
"If you register before reaching the limit, it can help your business. You can get back input VAT on big costs, like studio rent, materials, and art shipping or insurance. This helps your cash flow and lets you use special VAT plans." — Julien Lacroix, US Operations General Manager, Convelio
Check these official sites for the latest rules in the EU and UK:
Legislation | Description |
|---|---|
Council Directive 2006/112 | |
DG Taxation and Customs Union | Makes sure VAT rules are followed. |
Taxable Transactions | Covers goods, services, trade between EU countries, and imports. |
FAQ
How do you find the HS code for your product?
You can search for your product in the EU Tariffs Database. Fishgoo helps by matching your product link to the right HS code. This code tells customs what your item is and what duty rate applies.
Do you pay VAT and duties on every import?
Yes, you pay both VAT and duties when you import goods into the EU. Customs checks your shipment and calculates the taxes based on your product’s value and type.
What documents do you need for customs clearance?
You need an invoice, shipping details, and a customs declaration. Fishgoo provides these documents for your order. Customs uses them to check your goods and process your shipment.
Can you estimate duties and VAT before buying?
You can use online calculators or official databases to estimate costs. Fishgoo shows you product details and helps you find duty rates. This lets you plan your budget before you place an order.
See Also
Calculating Your Shipping Expenses with Fishgoo's Tools
Utilizing Fishgoo's Calculator for Precise Shipping Cost Estimates
Employing Fishgoo's Calculator for Global Shipping Cost Accuracy
Top Shipping Paths from China to Spain: Expenses and Tips
Enhancing Your International E-Commerce Logistics for Success


